PCB Assembly Process Flow: From Bare Board to Finished Product
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is an essential component of electronic devices, acting as a support structure and electrical connection carrier for electronic components. The PCB manufacturing process involves printing conductive circuits on insulating substrates, creating the printed lines that connect components.

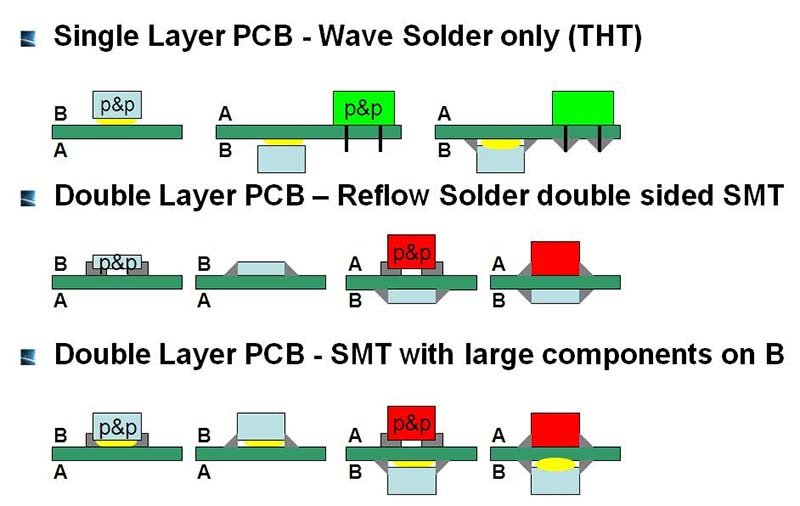
PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) refers to the process of assembling electronic components onto a PCB, which can only be counted as finished after all assembly processes are complete. PCBA involves surface-mount technology (SMT) and through-hole technology (THT), including solder paste printing, pick-and-place assembly, reflow soldering, wave soldering, testing, and quality inspection.
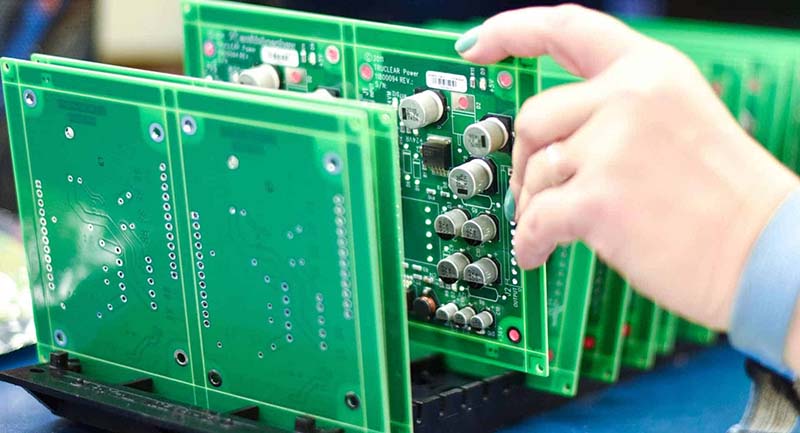
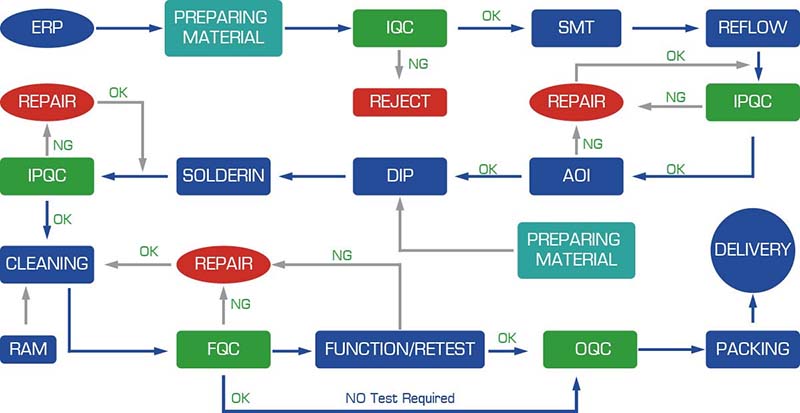
The PCBA process flow chart can vary, depending on factors such as the type of PCB board, production technology, and complexity of the design. Here are some common types of PCBA production flows:
Single-sided SMT Mounting:
Single-sided DIP Interfacing:
Single-sided Mixed Assembly:
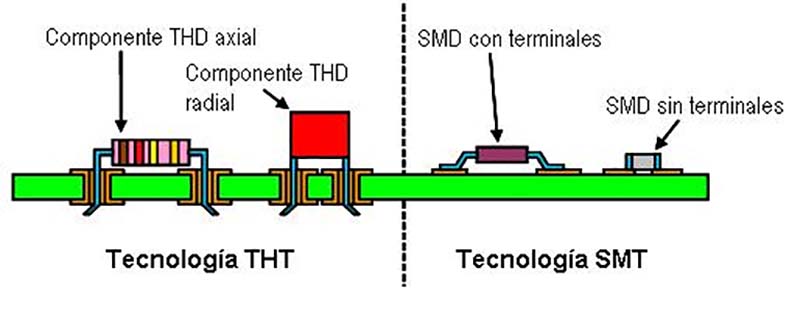
Single-sided Mounting and Cartridge Mixing:
Double-sided SMT Mounting:
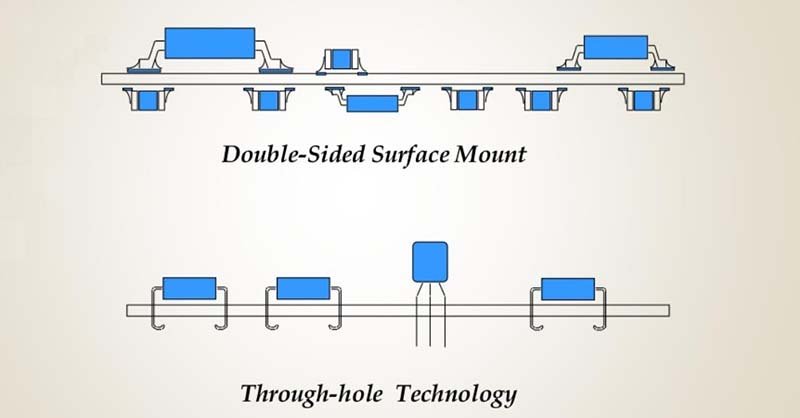
Double-sided Mixed Assembly:
When seeking PCBA assembly and processing manufacturers, it is crucial to choose experienced providers with high levels of processing equipment. The quality of solder joints on electronic components determines the quality of the PCBA board. Thus, manufacturers should ensure that their assembly process and production processes are optimized to produce high-quality finished products.


