In today’s rapidly advancing technological era, the electronic manufacturing services (EMS) industry is experiencing unprecedented transformation and growth. As part of this industry, we are excited to share the latest market insights and future outlook with you. This article will delve into global trends, market dynamics, technological innovations, and future opportunities in the EMS industry, providing you with a comprehensive industry perspective.
Market Overview and Growth Forecast
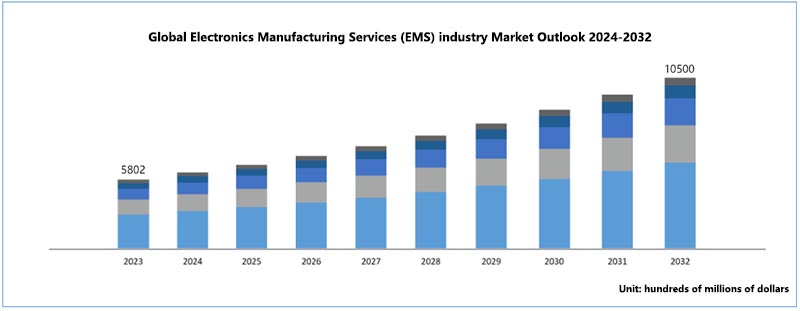
According to the latest industry report, the global EMS market is showing strong growth. in 2023, the global market size has reached US$580.2 billion, and is expected to grow to US$1,050.0 billion by 2032, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.8%. This significant growth reflects the growing demand for electronics across industries and the reliance of businesses on specialised manufacturing services.
Asia Pacific continues to maintain its position as the world’s largest EMS market, with a market size of $258.8 billion by 2023. The dominance of this region is mainly attributed to its cost-competitive labour force, well-established supply chain network, and favourable government policies.
2、Service Type Segmentation
The EMS industry offers a wide range of services, including but not limited to:
- Electronics Manufacturing: Core business, covering the production of electronic products from simple to complex.
- PCB Assembly: Assembly of printed circuit boards, a key aspect of electronic product manufacturing.
- Cable assembly: Customised cable solutions for a wide range of electronic devices.
- Electromechanical Assembly: Complex assembly services combining mechanical and electronic components.
- Testing services: including component level testing, circuit assembly testing and fully assembled unit testing to ensure product quality and reliability.
- Prototyping: Rapid prototyping to accelerate time-to-market.
- Engineering Services: Provide professional engineering support such as circuit design and PCB layout.
Test and Development Implementation: Develop and implement comprehensive test strategies to ensure product performance.
These diverse services enable EMS providers to offer customers a full range of solutions to support the entire process from conceptual design to final product delivery.

3、Key Application Areas
The EMS industry serves a number of key sectors, each with its own unique needs and growth opportunities:
- Consumer electronics: smartphones, tablets, smart home devices, etc.
- Aerospace & Defence: avionics systems, communications equipment, military electronics.
- Medical & Healthcare: diagnostic devices, medical monitors, wearable health devices.
- Automotive: in-vehicle infotainment systems, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), electric vehicle electronic systems.
- Semiconductor Manufacturing: Professional manufacturing services for the semiconductor industry.
- Robotics: Electronic systems for industrial robots and service robots.
- Agriculture: precision agriculture equipment, agricultural IoT equipment.
- Power & Energy: smart grid equipment, renewable energy system controllers.
These diverse application areas not only demonstrate the vast market for the EMS industry, but also highlight the technological challenges and innovation opportunities facing the industry.
4、Market Drivers and Industry Trends
Several key factors are driving the growth of the EMS market:
- Increasing demand for outsourcing: more and more original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) are opting to outsource electronics manufacturing to focus on core competencies.
- Efficiency and cost optimisation: EMS providers are able to achieve cost efficiencies through economies of scale and specialised production.
- Increased technological complexity: The increasing complexity of electronic products requires specialised manufacturing capabilities.
- Demand for fast time-to-market: Competitive markets require shorter product development cycles.
We have also observed the following industry trends:
- End-to-end solutions: EMS providers are expanding their service offerings to provide comprehensive solutions from design to aftermarket.
- Enhanced engineering services: More and more EMS companies are offering high value-added engineering services, including product design and development.
- Flexible Manufacturing: Flexible manufacturing capabilities to adapt to the demands of multi-variety and small-lot production are becoming a competitive advantage.
- Smart manufacturing: the application of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence and big data analytics.
- Sustainable development: the adoption of green manufacturing and circular economy models is becoming increasingly important.
5、Technological Innovation and Future Outlook
Technological innovation is reshaping the future of the EMS industry:
- Automation and Robotics: Increasing productivity and precision and reducing human error.
- 3D printing: accelerates prototyping and supports low-volume production.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Optimise production processes and predict maintenance requirements.
- 5G technology: supports more efficient communication and data transmission, facilitating the development of smart factories.
- Blockchain: improves supply chain transparency and traceability.
In the future, we expect the following areas to be key areas of development for the EMS industry:
- Highly customised production: the ability to meet individual requirements will become a key competency.
- Cybersecurity: with the proliferation of IoT devices, product security will become a top priority.
- Sustainable manufacturing: environmentally friendly materials, energy-efficient processes and circular economy models will be more widely used.
- Digital twin technology: Virtual simulation and real-time monitoring will further optimise production processes.
- Cross-industry co-operation: EMS providers will cooperate deeply with experts from various industries to develop innovative solutions.

6、Regional Market Analysis
While Asia-Pacific remains the dominant force in the EMS industry, other regions are showing unique opportunities:
- North America: Strong demand in high-end electronics, medical devices and defence electronics.
- Europe: Increased opportunities in automotive electronics, industrial automation and renewable energy.
- Latin America: Rapid growth in the consumer electronics market is creating new opportunities for EMS providers. The region is becoming a major manufacturing centre, particularly in Brazil and Mexico.
- * Middle East and Africa: as industrialisation accelerates in these regions, demand for electronics manufacturing services is increasing, particularly in the telecommunications and automotive sectors.
Technology trends and innovations
The EMS industry is undergoing a technological revolution, which is reshaping manufacturing processes and service delivery:
1、Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing:
- The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is improving productivity and quality control.
- Digital twin technology allows real-time monitoring and optimisation of production lines.
- Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and improves overall equipment efficiency (OEE).
2、Additive manufacturing (3D printing):
- Rapid prototyping and small batch production become more affordable.
- The production of complex geometric shapes becomes possible, bringing new possibilities for product design.
3、Flexible automation:
- The increased use of collaborative robots (cobots) has improved production flexibility.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) optimise logistics within factories.
4、5G technology:
- High-speed, low-latency communications support more efficient factory operations.
- Provides new possibilities for remote monitoring and control.
5、Blockchain in supply chain management:
- Improves supply chain transparency and traceability.
- Helps to combat counterfeit products and protect intellectual property rights.
Sustainable development and environmental responsibility
As global attention to climate change and environmental protection continues to grow, the EMS industry is actively responding to this trend:
1、Green Manufacturing:
- Reduce carbon footprint by adopting energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources.
- Implement waste reduction and recycling programmes.
2、Circular Economy Model:
- Design products that are easy to recycle and reuse.
- Provide product refurbishment and remanufacturing services.
3、Environmentally friendly materials:
- Use biodegradable materials and recycled plastics.
- Reduce the use of hazardous substances, such as lead-free solder.
4、Supply chain sustainability:
- Co-operate with environmentally friendly suppliers.
- Optimise logistics and reduce carbon emissions during transportation.
5、Energy Management:
- Implement intelligent energy management systems.
- Invest in efficient manufacturing equipment.
- These sustainability initiatives are not only good for the environment, but also help EMS providers reduce costs, improve efficiency, and meet the needs of a growing number of environmentally conscious customers.

Market Challenges and Strategies to Address Them
Despite the bright future of the EMS industry, there are still some challenges:
1、Supply chain disruption:
- Challenge: Global events (e.g., epidemics, geopolitical conflicts) may lead to supply chain disruptions.
- Strategies: Diversify supply sources, establish local supply networks, and increase inventory buffers.
2、Skills shortage:
- Challenge: Shortage of highly skilled workers, especially in emerging technologies.
- Strategy: Invest in employee training, partner with educational institutions, and implement automation to bridge the skills gap.
3、Rapidly changing technology:
- Challenge: Keep pace with technological advances to remain competitive.
- Strategy: continue to invest in R&D and establish strategic alliances with technology partners.
4、Price pressure:
- Challenge: Customers are demanding lower prices while maintaining high quality.
- Strategy: Improve efficiency through automation and lean manufacturing, and provide value-added services to differentiate from competitors.
5、Intellectual Property Protection:
- Challenge: Protect customers’ intellectual property rights in a globalised environment.
- Strategy: Implement strict security measures and use technologies such as blockchain to enhance traceability.
6、Environmental regulations:
- Challenge: Comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
- Strategy: Proactively adopt green technologies and make sustainability a core business strategy.
Future Outlook.
Looking ahead, the EMS industry will continue to evolve and adapt to new market demands and technological advances:
1、Personalised manufacturing: As consumer demand for customised products increases, EMS providers will need to develop more flexible production lines that can cost-effectively handle small-volume, highly personalised orders.
2、Edge computing and 5G: With the rollout of 5G networks and the rise of edge computing, EMS companies will need to adapt to produce devices with higher computing power and connectivity.
3、Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: These technologies will play an increasingly important role in quality control, predictive maintenance and supply chain optimisation.
4、Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR): These technologies will be used for training, remote assistance and product design to improve efficiency and innovation.
5、Cybersecurity: as manufacturing becomes more digital and connected, cybersecurity will become a key consideration. ems providers will need to invest in robust security measures to protect sensitive data and intellectual property.
6、Bio-electronics: as medical technology advances, the demand for bio-electronic devices will increase, opening up new growth areas for the EMS industry.
7、Space technology: with the rise of commercial space exploration, the demand for high-reliability, extreme environments will increase the demand for electronic products. EMS providers will need to develop specialised manufacturing capabilities to meet the needs of this emerging market.
8、Sustainable development: environmental awareness will promote EMS companies to adopt more sustainable manufacturing practices, including the use of recyclable materials, reduce energy consumption and waste generation.
9、Smart Factory: Widespread adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies will drive EMS factories to transform into fully automated and highly connected smart factories, improving efficiency and flexibility.
10、Blockchain technology: This may be used to improve supply chain transparency and traceability, helping to combat counterfeit products and improve quality control.
11、3D printing: With the advancement of 3D printing technology, it may play a greater role in prototyping and small-volume production.
12、Quantum computing: Although still in its early stages, quantum computing could have a profound impact on electronic product design and manufacturing, and EMS companies need to pay close attention to developments in this area.

Overall, the future of the EMS industry will be more focused on flexibility, innovation and sustainability. Successful EMS providers will need to continually invest in new technologies, develop highly skilled personnel and work closely with customers to respond to changing market demands. At the same time, they will need to strike a balance between globalisation and localisation to optimise cost efficiency and supply chain resilience.


