PCB assembly refers to the process of assembling electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB). The purpose of PCB assembly is to create functional and reliable electronic devices that can perform specific tasks, such as controlling power, transmitting data, or executing computational functions.

PCB assembly involves several processes, including the following:
- Solder Paste Application: This process involves applying solder paste to the surface of the PCB where the components will be placed. The solder paste acts as a temporary adhesive for the components before they are permanently soldered.

- Pick-and-Place: In this process, automated machines pick up electronic components from reels, trays, or tubes and place them onto the PCB using precise positioning systems. These machines can handle small components such as resistors and capacitors as well as larger ICs and connectors.

- Reflow Soldering: This process involves heating the PCB and components in a reflow oven to melt the solder paste and create a permanent joint between the component leads and the pads on the PCB.

- Through-Hole Assembly: Some components cannot be mounted using surface mount technology (SMT) and require through-hole assembly. In this process, the components are inserted into holes drilled into the PCB and then soldered on the other side.
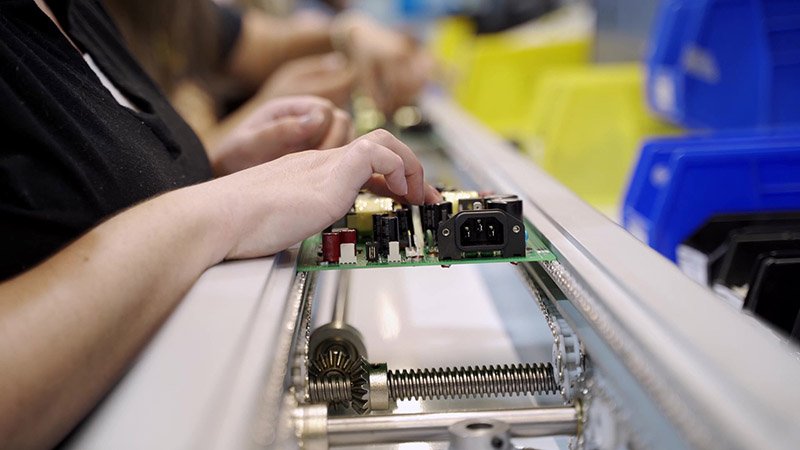
- Inspection and Testing: After assembling the PCB, it undergoes inspection and testing to ensure that all the components are correctly placed, and no defects or faults are present. Several tests are conducted, including visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI), and functional testing.
Some important considerations for PCB assembly include:
- Design for Manufacturability: It’s essential to design your PCB with manufacturability in mind. Consideration should be given to aspects such as component placement, orientation, and spacing, trace routing, and via placement. A good design-for-manufacturing (DFM) strategy can reduce costs, improve quality, and shorten production lead times.

- Component Selection: Selecting the right components is crucial for ensuring that your electronic device functions reliably and meets performance requirements. Consideration should be given to factors such as compatibility with other components, durability, availability, and cost.
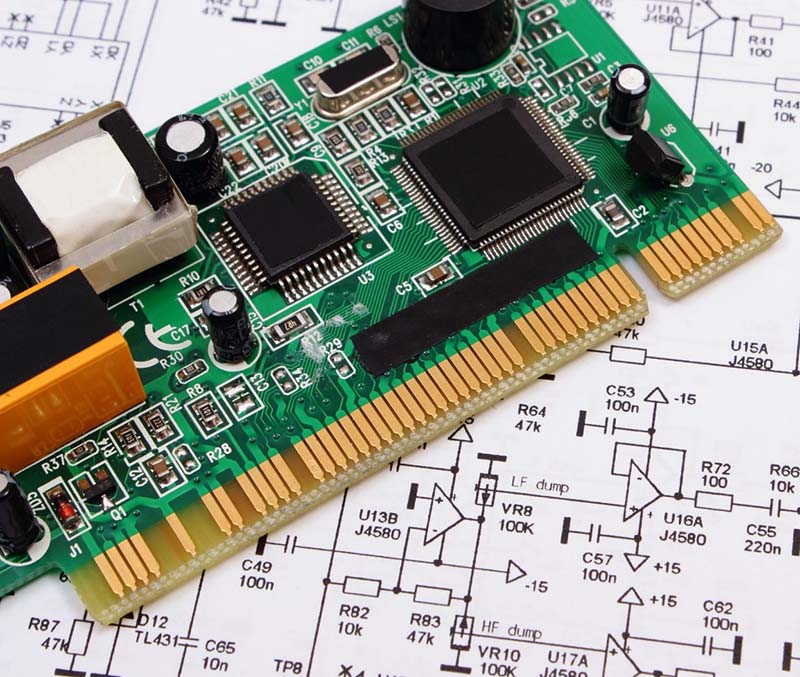
- Quality Control: Quality control measures are essential for ensuring that the finished product meets the required standards. Inspection and testing procedures should be implemented throughout the assembly process to identify any defects or faults before shipment.

- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration can affect the reliability and lifespan of electronic devices. It’s essential to consider these factors when selecting components and designing the PCB.

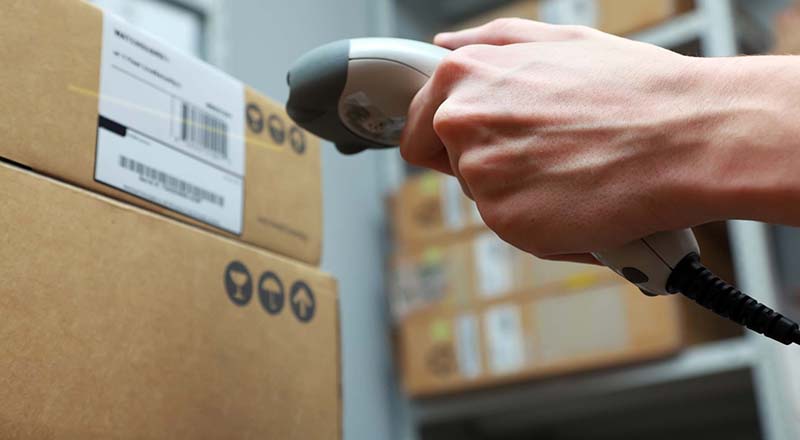
- Packaging and Shipping: Proper packaging and shipping practices are essential for protecting your finished products during transport. The packaging should provide adequate protection against shock, vibration, and moisture, and appropriate labeling and documentation should be provided.

In conclusion, PCB assembly is a critical process in the development of electronic devices. It involves several processes, including solder paste application, pick-and-place, reflow soldering, through-hole assembly, and inspection and testing. To ensure successful PCB assembly, it’s important to consider design-for-manufacturing strategies, component selection, quality control, environmental factors, and packaging and shipping practices. With careful planning and attention to detail, you can create reliable and functional electronic devices that meet your specific needs.


